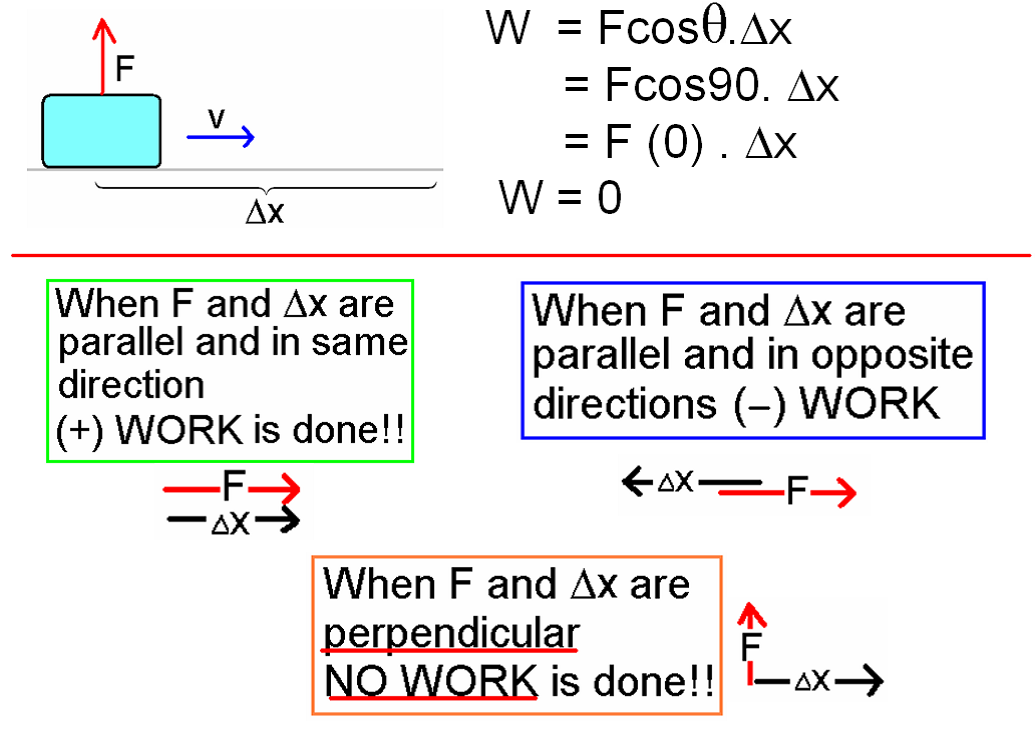
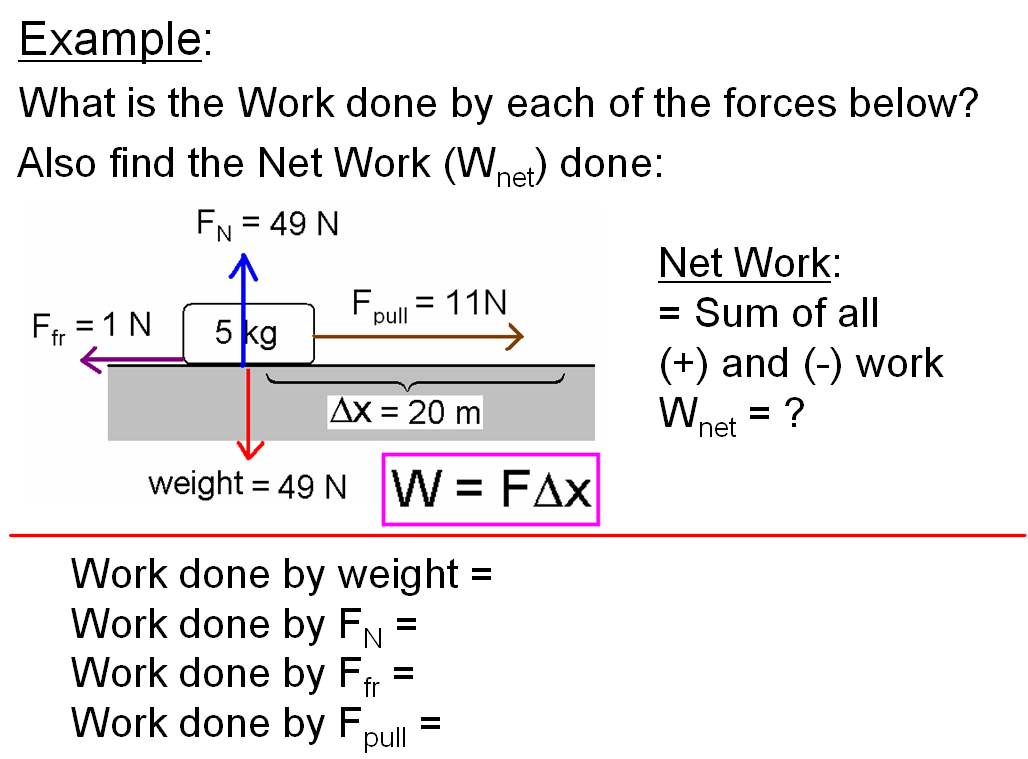
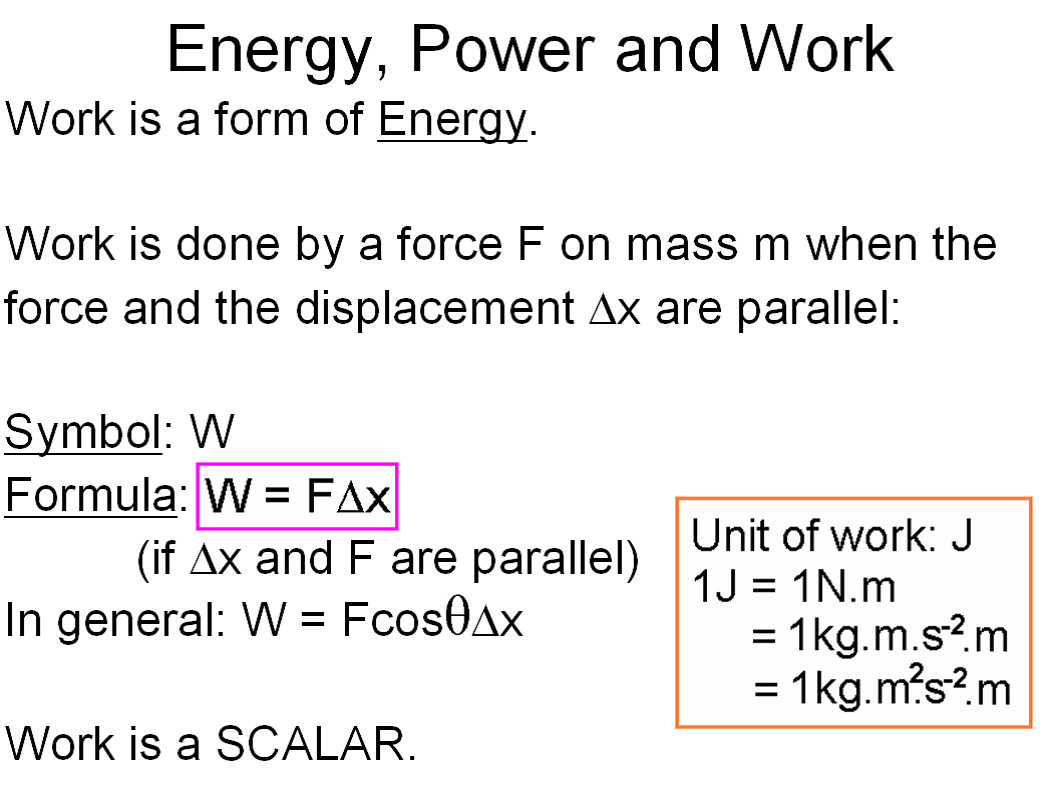
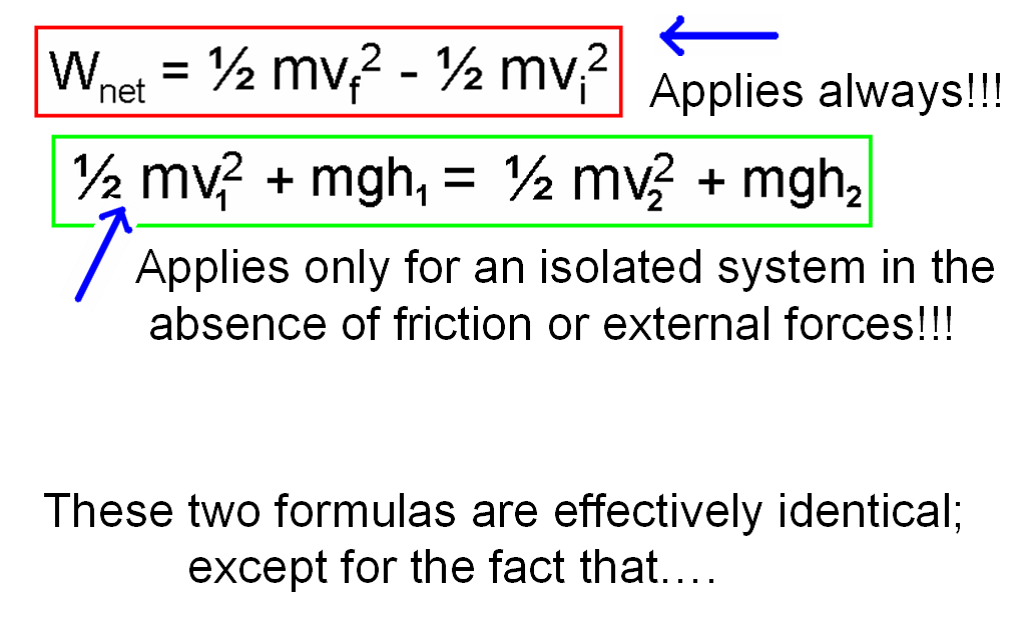
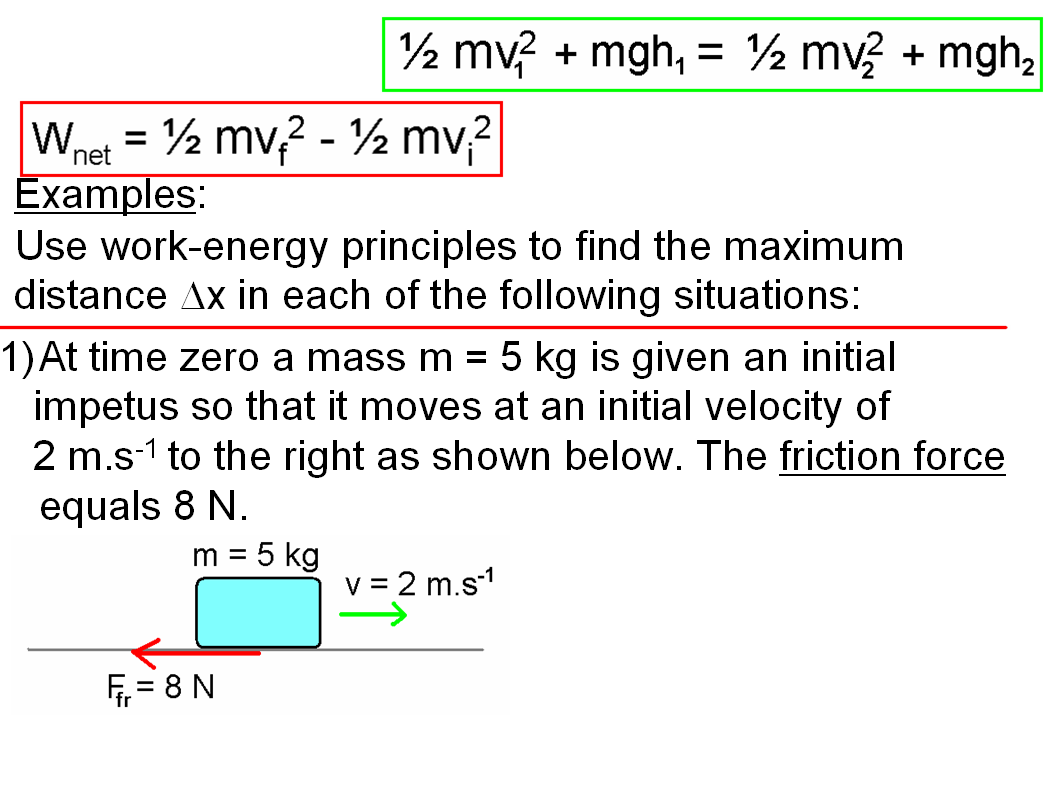
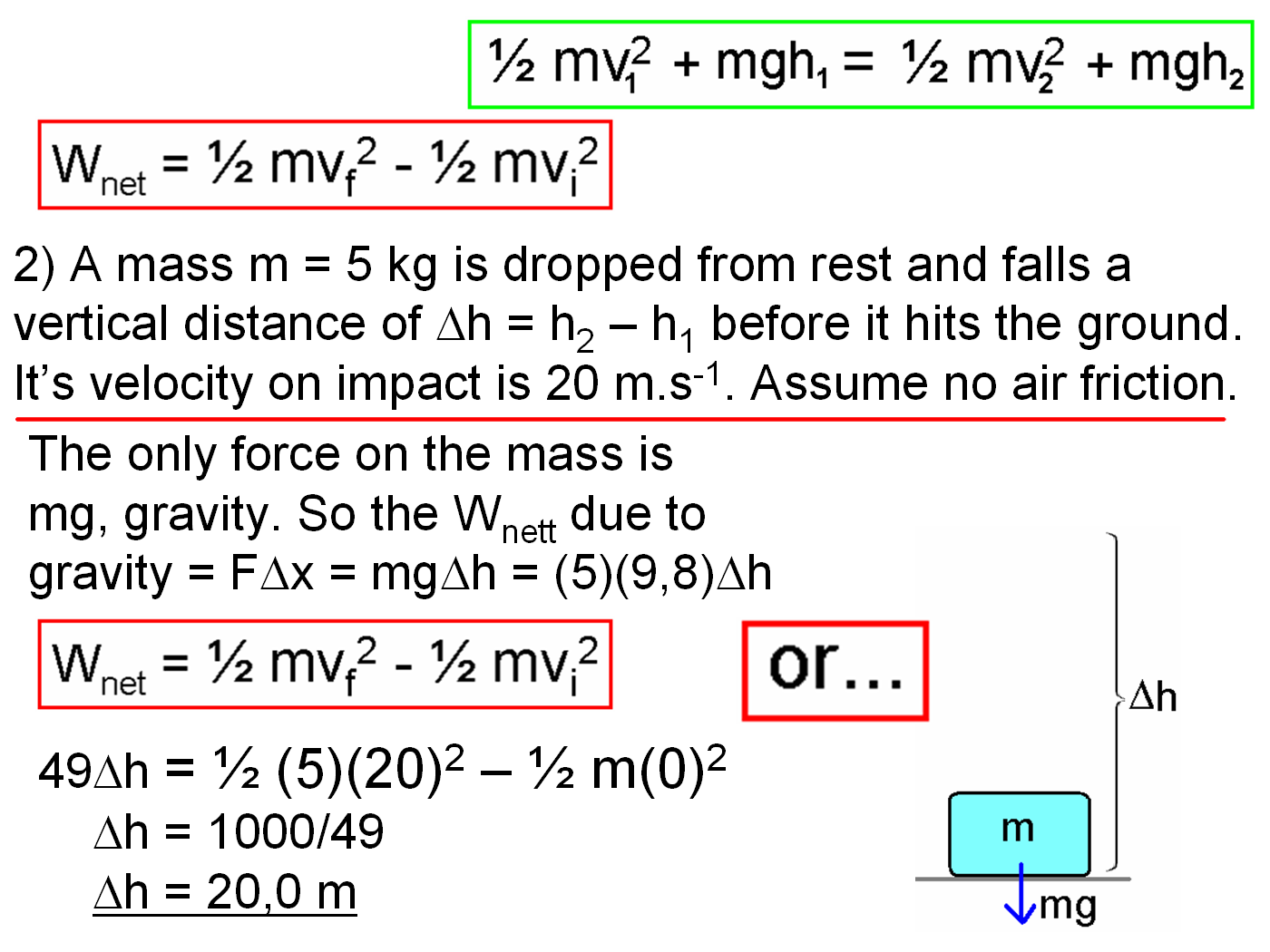
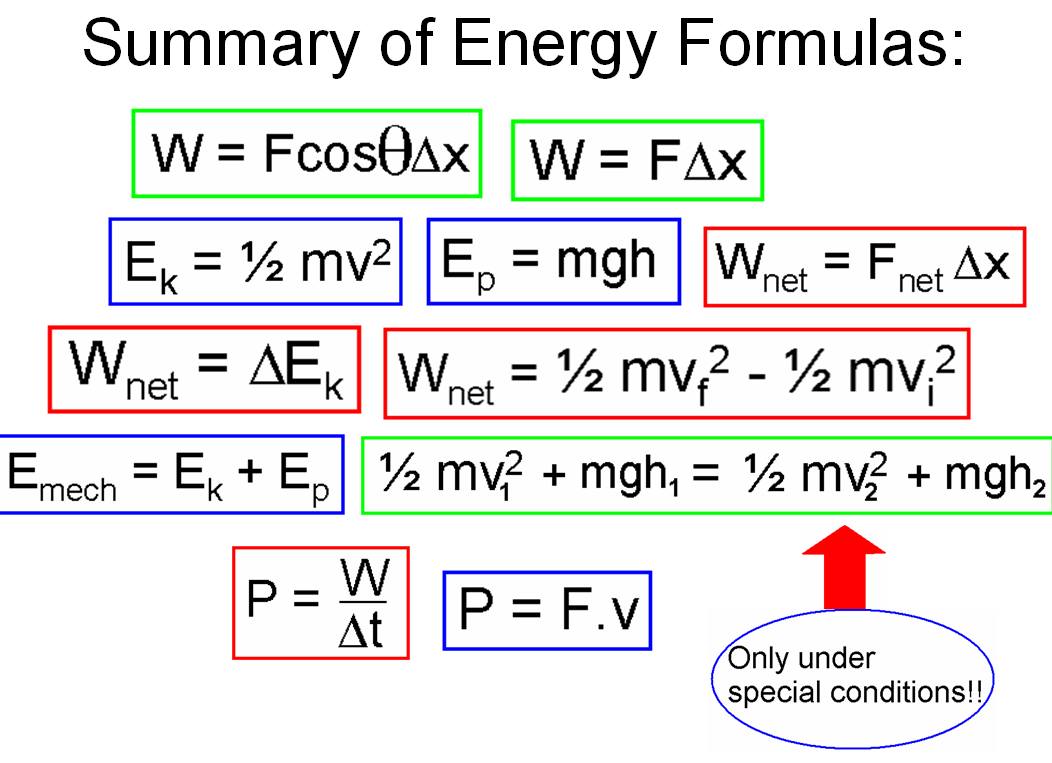
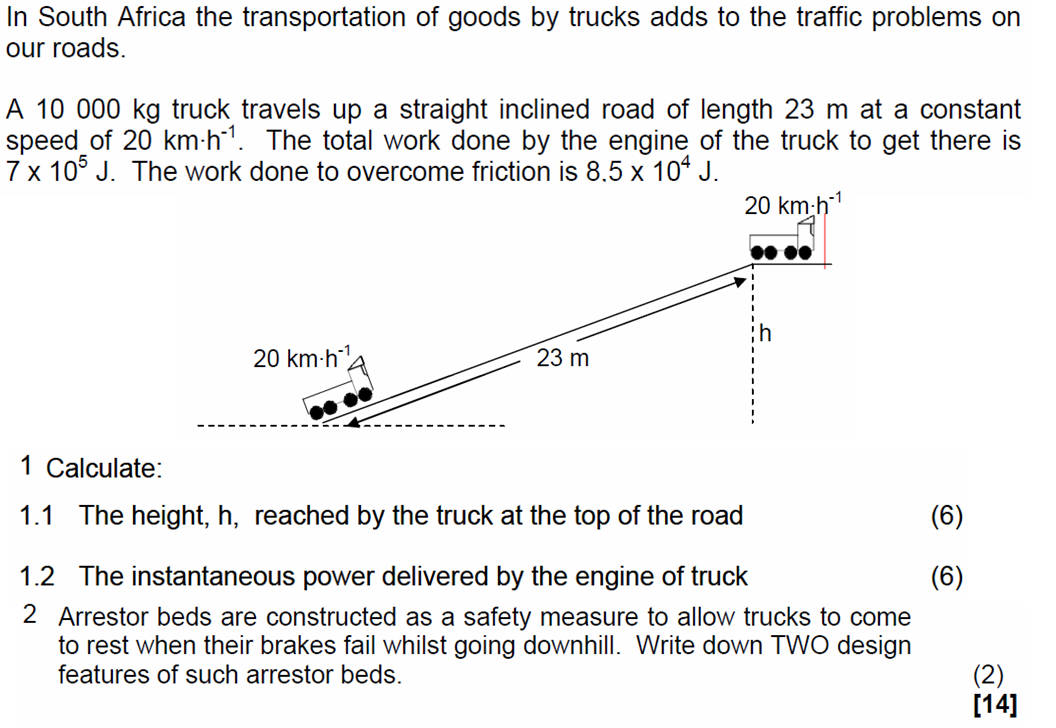
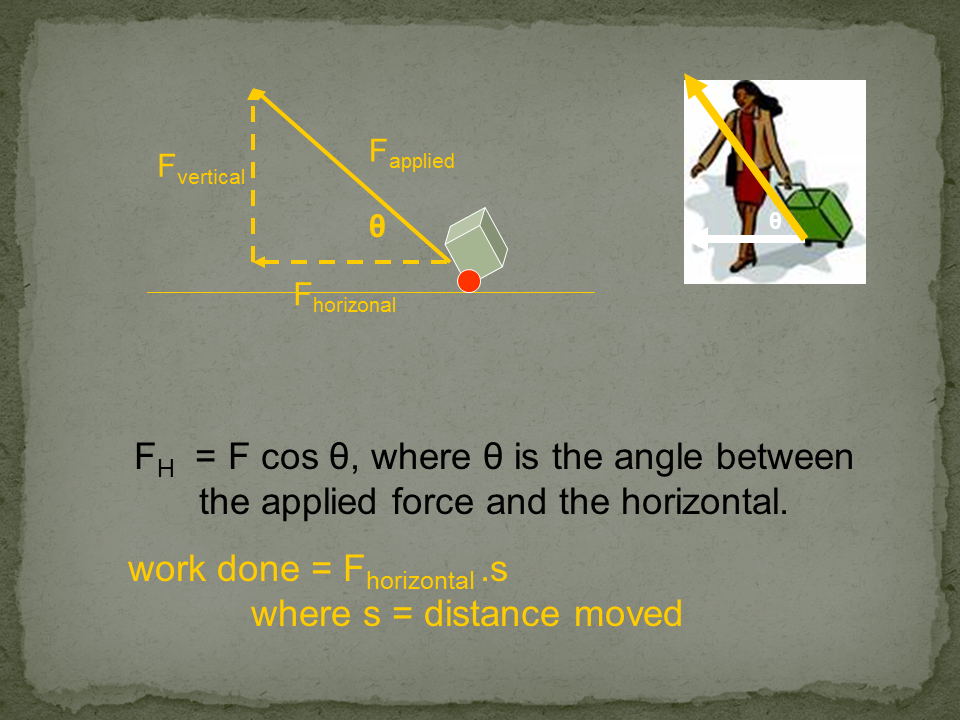
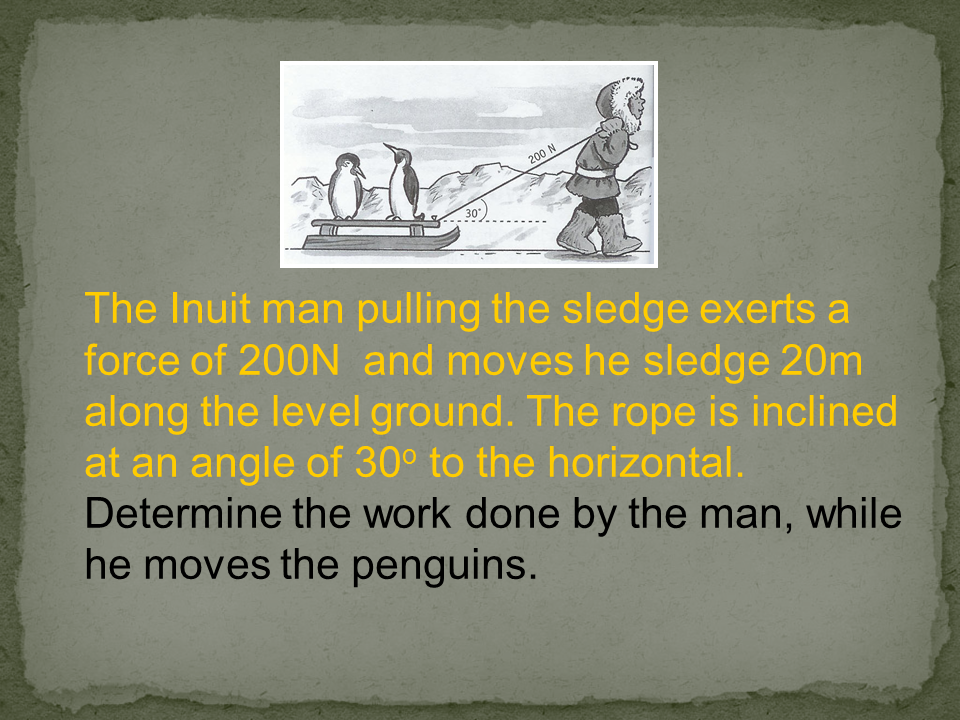
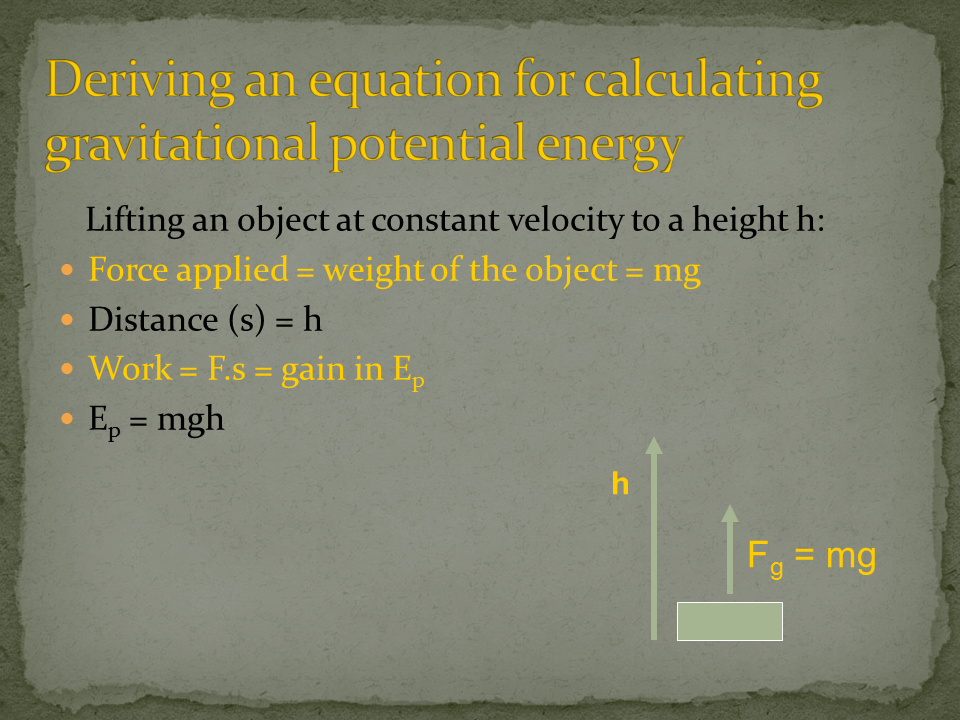
Work: In physics, work is defined as the product of force and displacement when the force is acting in the direction of the displacement. Mathematically, work W is given by the equation W=Fxs, where F is the force applied and s is the displacement. Work is a scalar quantity and is measured in joules (J).
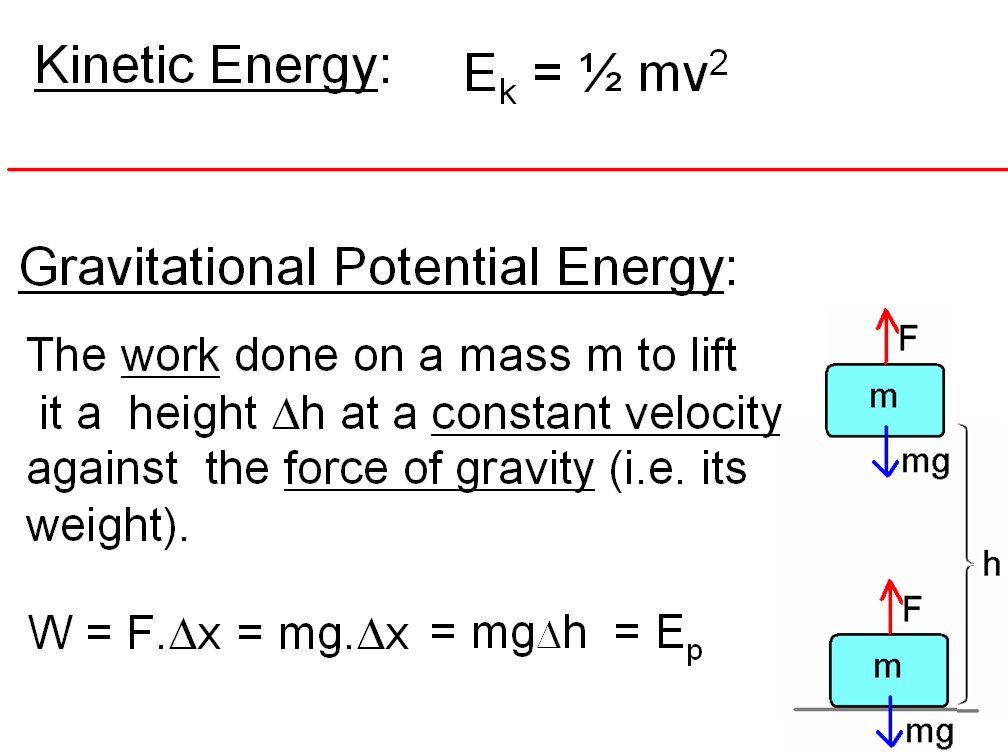
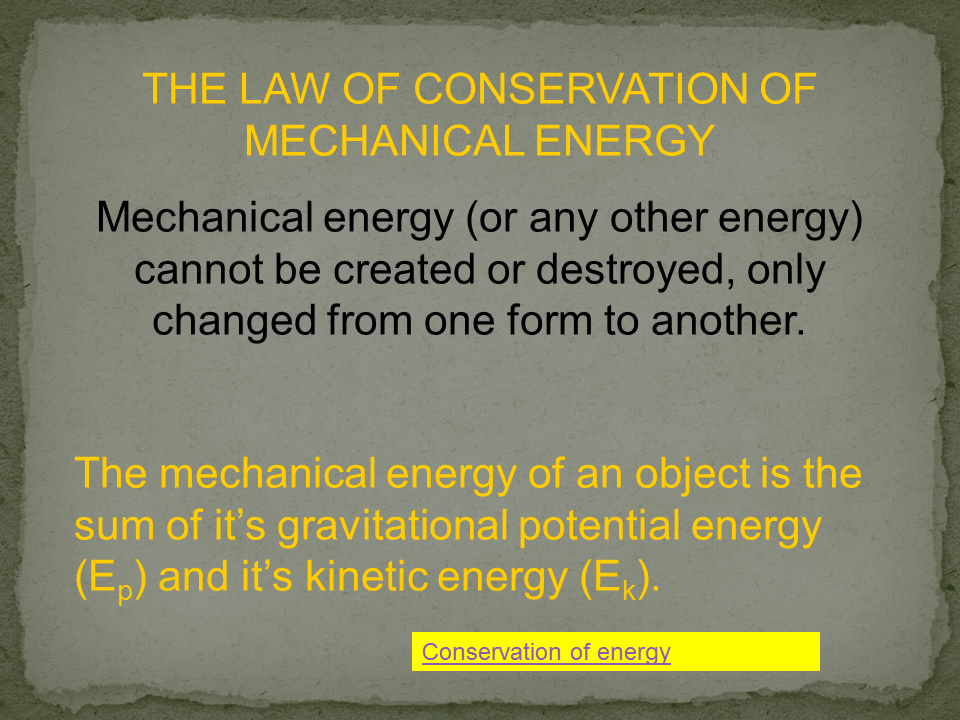
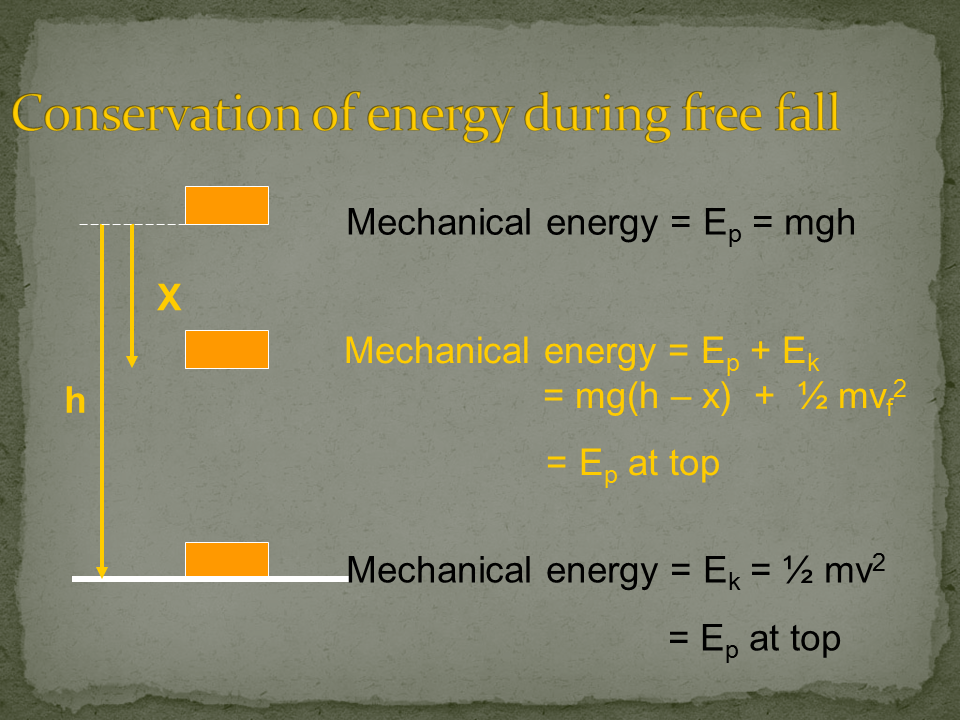
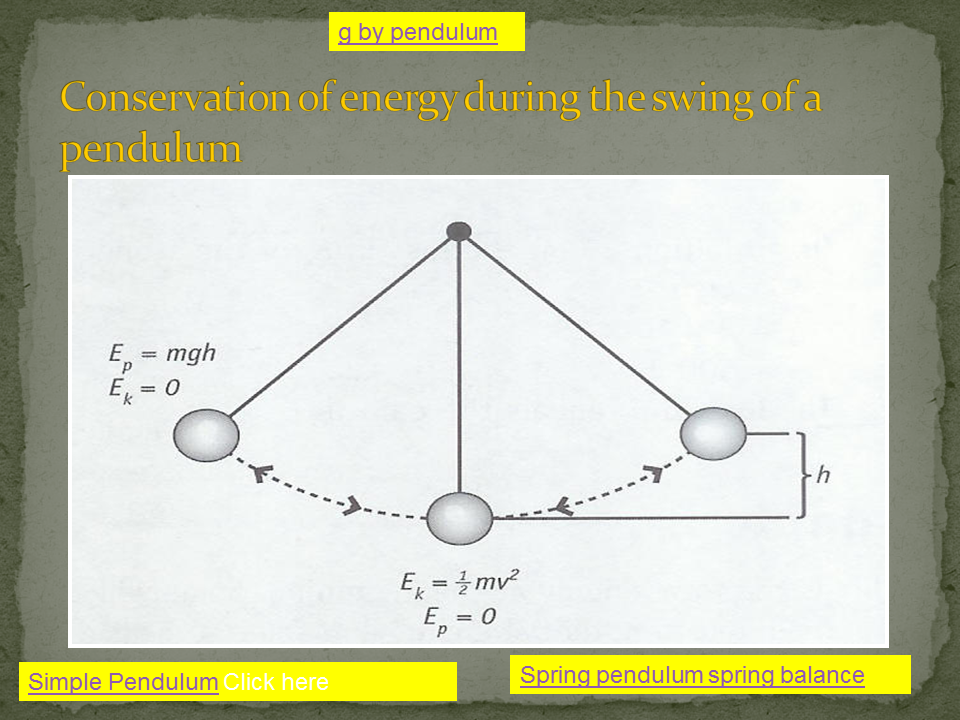
Energy: Energy is the capacity to do work. There are various forms of energy, including kinetic energy (energy of motion), potential energy (stored energy), thermal energy (heat energy), chemical energy (energy stored in chemical bonds), and more. The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
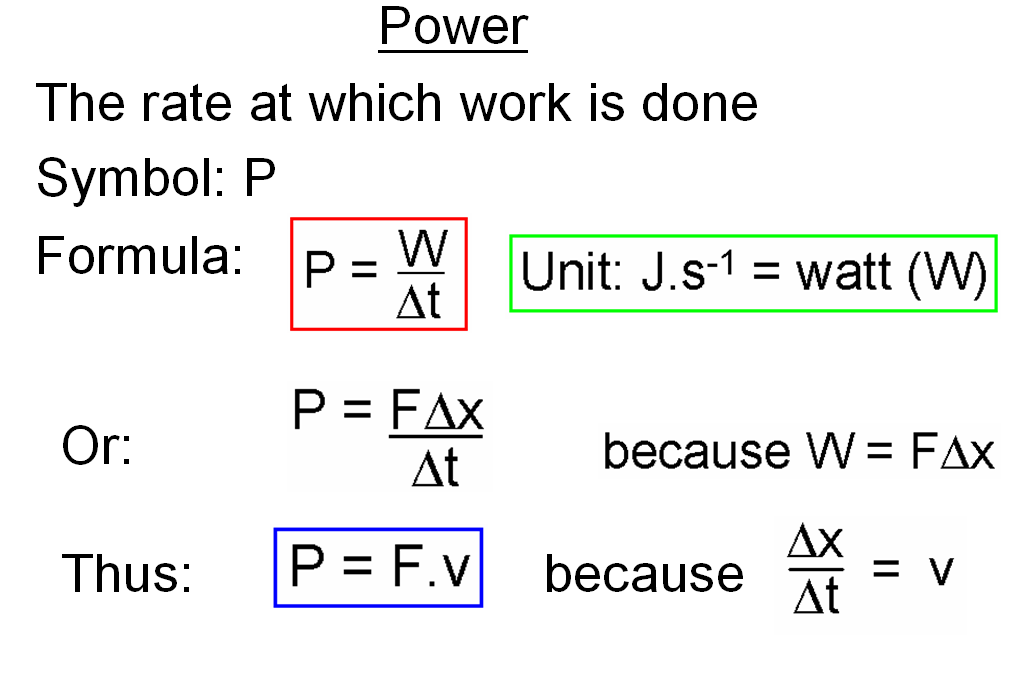
Power: Power is the rate at which work is done or the rate at which energy is transferred or converted. Mathematically, power P is defined as P=W/t, where W is the work done and t is the time taken. Power is measured in watts and is a measure of how quickly work is done or energy is transferred.